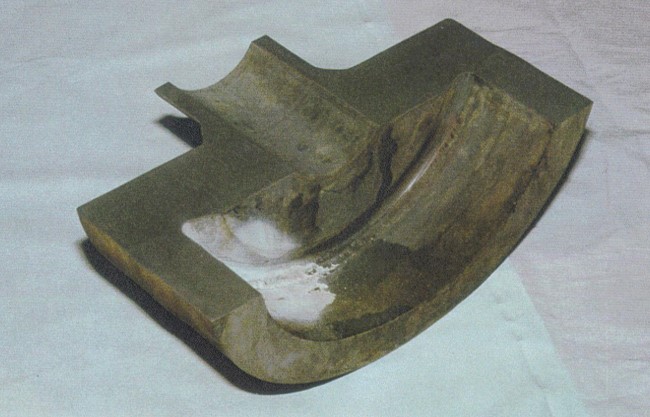

Component:
- Header, fabricated from P91, with welded-on, flat-plate end-caps
Problem:
- Explosive failure of an end-cap weld
Approach:
- Failure analysis, fracture mechanics assessment and design review
Results:
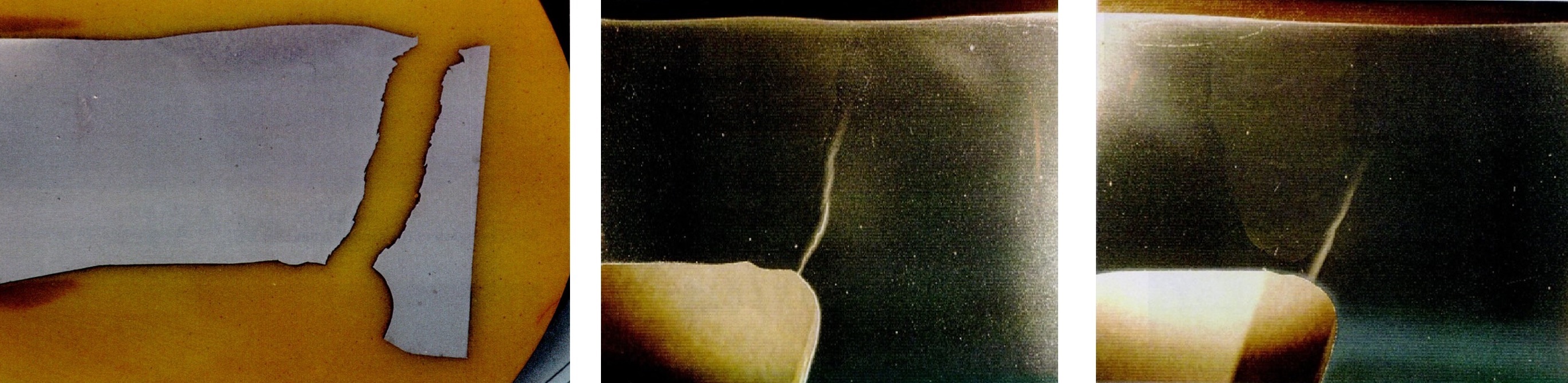
- Failure shown to result from Type IV cracking, initiating at a radius in the end-plate side of the weld preparation
- NDE of other headers revealed a 1/3 wall crack in another end-cap weld
- Sectioning of another weld, that was NDE clear, revealed extensive Type IV cavitation damage
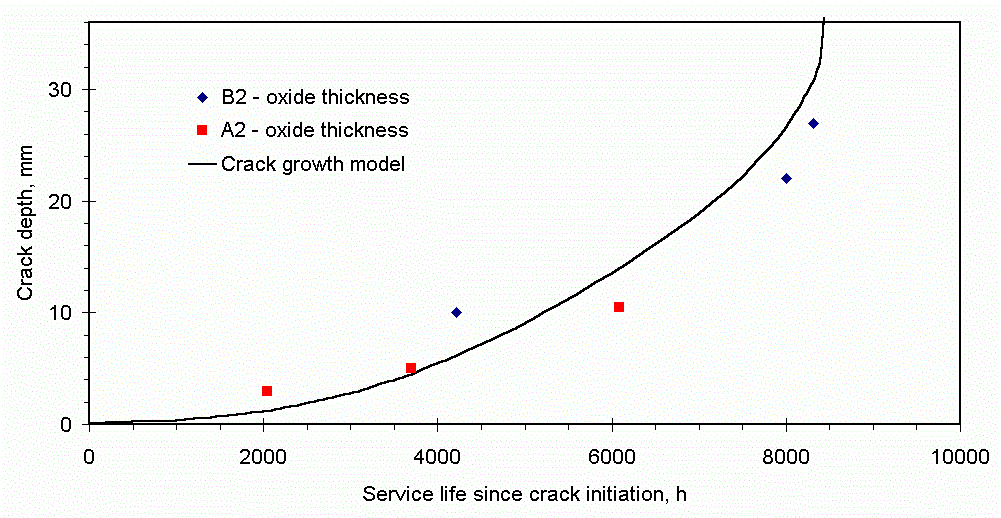
- Fracture mechanics assessment indicated crack growth from initiation to failure in less than 10,000 hours, confirmed by oxide crack-dating. Thus adequate life could not be demonstrated
- Design changes identified that would separate the weld HAZ from the stress concentration
Benefits:
- Root cause of failure identified
- Design changes to alleviate problem proposed
Further research by the utility indicated a need for tighter controls on composition and heat treatment
Published:
Brear, J.M, Middleton, C.J., Munson, R and Viswanathan, R,
“Successful management of Type IV cracking in advanced 9% and 12% chromium steels”,
EPRI FRAC Conf ‘9Cr Materials, Fabrication and Joining Technologies’ Myrtle Beach, SC, July 2001
Brear, J.M.,
“A practical route for the life assessment of boiler pressure parts”
SMiRT 13 Post Conf Seminar ‘Intelligent Software Systems in Inspection and Life Management of Power and Process Plants’, Paris, 25-27 August 1997
