Component:
- Main steam pipework fabricated from advanced 9Cr steels
Objective:
- To determine the operating temperatures and timescales at which advanced steel pipework might be susceptible to Type IV cracking
Approach:
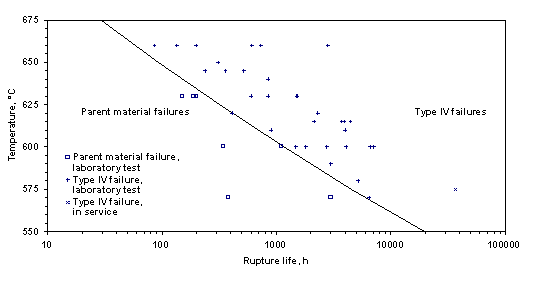
- Study of the known behaviour of CrMoV and X20 piping systems
- Cross-weld testing of advanced steels
Benefits:
- Determination of typical and critical system stresses
- Quantification of weldment strength relative to parent material, as a function of service conditions
- Production of maps for predicting weld failure location and time
- Definition of service conditions for which these steels are relatively immune to Type IV cracking
Published:
Brear, J.M.
“Weld life prediction – building on experience”
International VDI Conference ‘Alloys in Power Plant Technology’, Berlin 11-12 November 2014
“Weld life prediction – building on experience”
International VDI Conference ‘Alloys in Power Plant Technology’, Berlin 11-12 November 2014
Brear, J.M. and Fleming, A
“Prediction of P91 life under plant operating conditions”
ETD Int Conf ‘High Temperature Plant Integrity and Life Extension’ Robinson College, Cambridge, 14-16 Apr 2004
Middleton, C.J., Brear, J.M, Munson, R and Viswanathan, R
“An assessment of the risk of Type IV cracking in welds to header, pipework and turbine components constructed from the advanced ferritic 9% and 12% chromium steels”
3rd EPRI Conf ‘Advances in Material Technology for Fossil Power Plants’, Swansea, April 2001. EPRI Report 1001462. Inst Materials, London, Book 0770 pp.69-78
“An assessment of the risk of Type IV cracking in welds to header, pipework and turbine components constructed from the advanced ferritic 9% and 12% chromium steels”
3rd EPRI Conf ‘Advances in Material Technology for Fossil Power Plants’, Swansea, April 2001. EPRI Report 1001462. Inst Materials, London, Book 0770 pp.69-78
