
Plant:
- A 270 MW gas fired boiler, of once-through (Benson) type with 180,000h service.
- After 5 years base-load operation followed by 20 years of load following, the utility wishes to run in a two-shifting regime for 8 more years.
Objective:
A Phase 1 remaining life assessment of:
- all critical headers (22 types)
- some internal pipework (2 bends)
- some tubes (2 banks)
Basis of assessment:
- Current condition (calculated life consumed)
- operating conditions to date - Remaining life
- proposed change from load following to two shifting - Mechanisms
- low temperature headers - fatigue only
- high temperature components - creep and fatigue
- tubes - creep, fireside corrosion, steamside corrosion - Input data
- actual and expected operating conditions
- design materials data and dimensions - Code based stress analysis (TRD)
- all key locations
Operational events considered:
- Starts
- Cold to 40 MW
- Cold to full load
- Warm to full load
- Hot to full load
- Load changes
- 40 – 270
- 270 – 40 MW
- 80 – 160 MW
- 40 – 270 – 130 – 270 – 40 MW (full 24h cycle)
- Unit trip
Excursions and instabilities:
Known in advance:
- Economiser
- cold-water pull-through from de-aerator on run-up - Evaporator, level maintaining vessel, cyclones
- feedwater choke on transition to once-through operation
Discovered during the assessment:
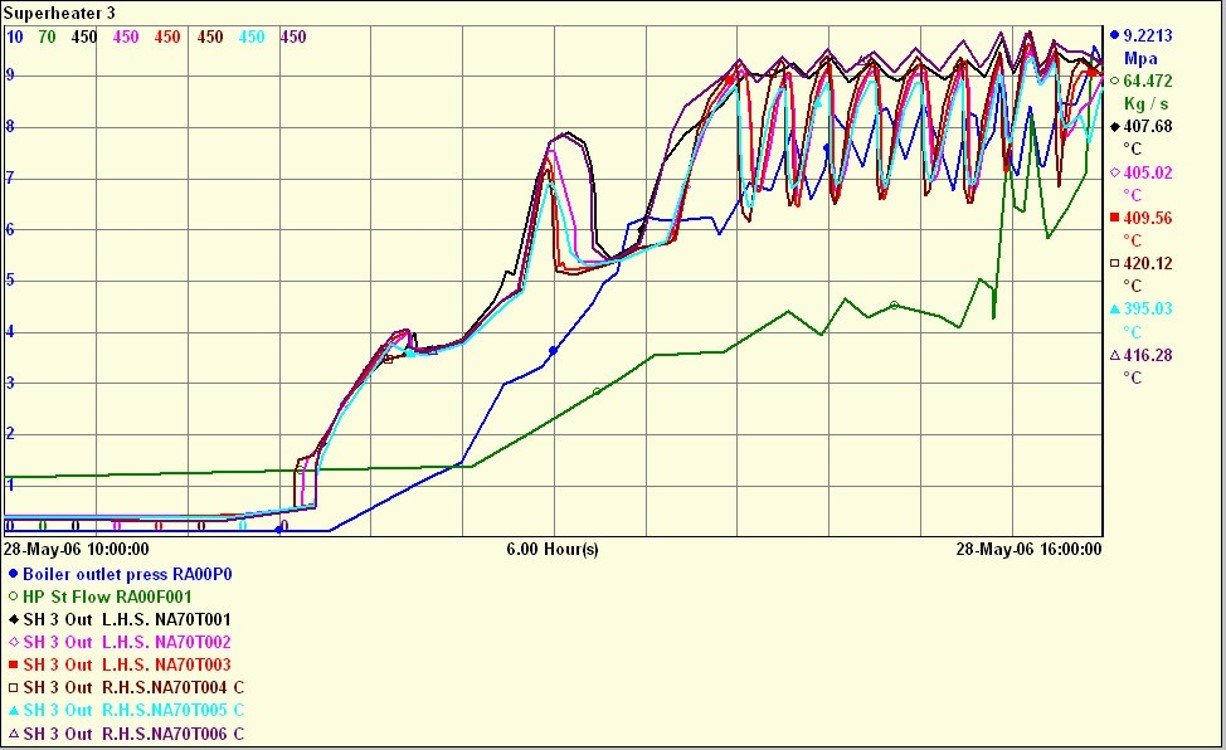
- Superheaters 3 and 4, Reheater 2
- Attemporator instability - Reheater 1
- Bypass instability
Results - fatigue:
- Two components were calculated to be fatigue critical at the assessment time
- If instabilities have their maximum effect, then a further component was also calculated to be fatigue critical at the assessment time
- Three components were calculated to become fatigue critical during the next 8 years
- If instabilities have their maximum effect, then a further component was also calculated to become fatigue critical during the next 8 years
Results - creep and fatigue combined:
- Two components were calculated to be creep strain critical at the assessment time
- One of these was also critical with regard to calculated total damage at the assessment time and the calculated total damage was predicted to exceed 1 within the next 8 years
- The other was predicted to become critical with respect to calculated total damage during the next 8 years
Recommendations:
- Further data, necessary to refine the assessment for those components which were predicted to become critical within the next 8 years, were identified
- Future inspection plans were formulated
- Scope and timing
- Techniques - Potential replacements were identified
